
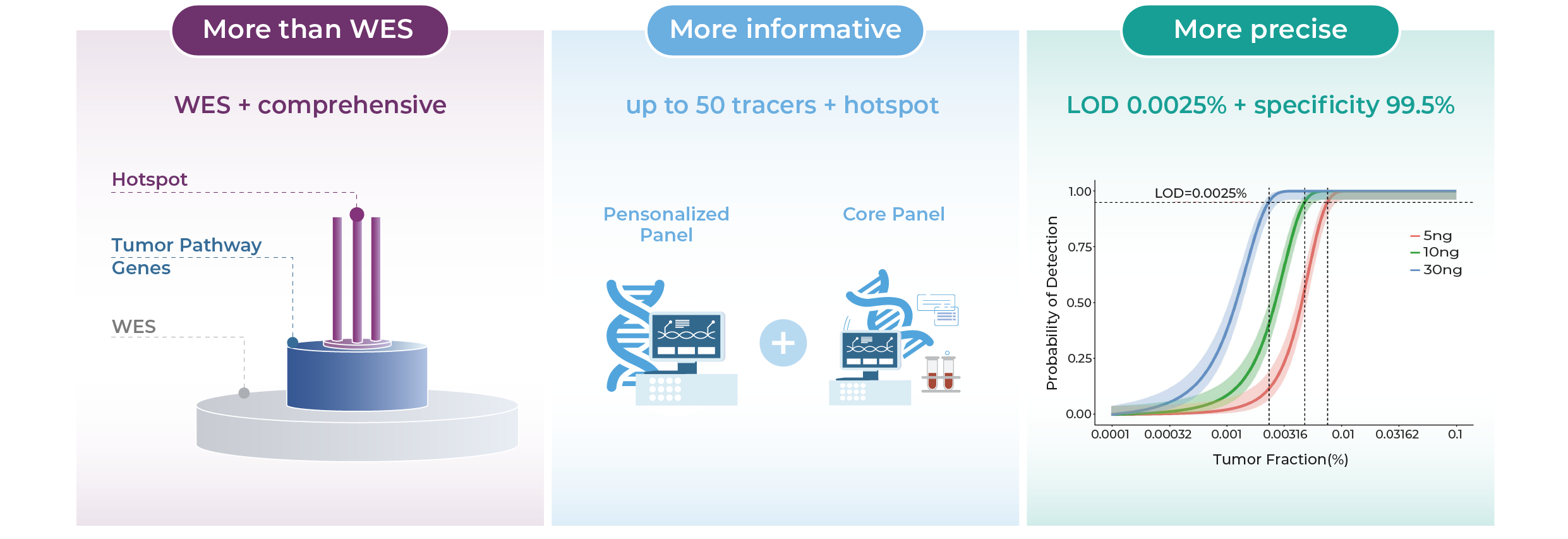
Ultra-sensitive (LoD 0.0025%) | Dual-panel architecture | Broad tumor coverage
A tumor-informed, ctDNA-based MRD assay designed for solid tumor management
Comprehensive. Sensitive. Clinically Actionable.
Track deeper. Act sooner.
Genecast MRD MinerVa Prime integrates personalized ctDNA tracking with a fixed-panel approach to deliver high-sensitivity MRD detection across solid tumors—supporting recurrence risk assessment, treatment monitoring, and resistance mutation tracking in a single solution.
Do you have questions when it comes to choosing a cancer treatment?
“Will I relapse after surgery?”
“Is this treatment truly effective for me?”
“Can I safely stop therapy now?”
“The scan shows no tumor—does that mean I’m completely safe?”
MRD can provide molecular answers beyond imaging.
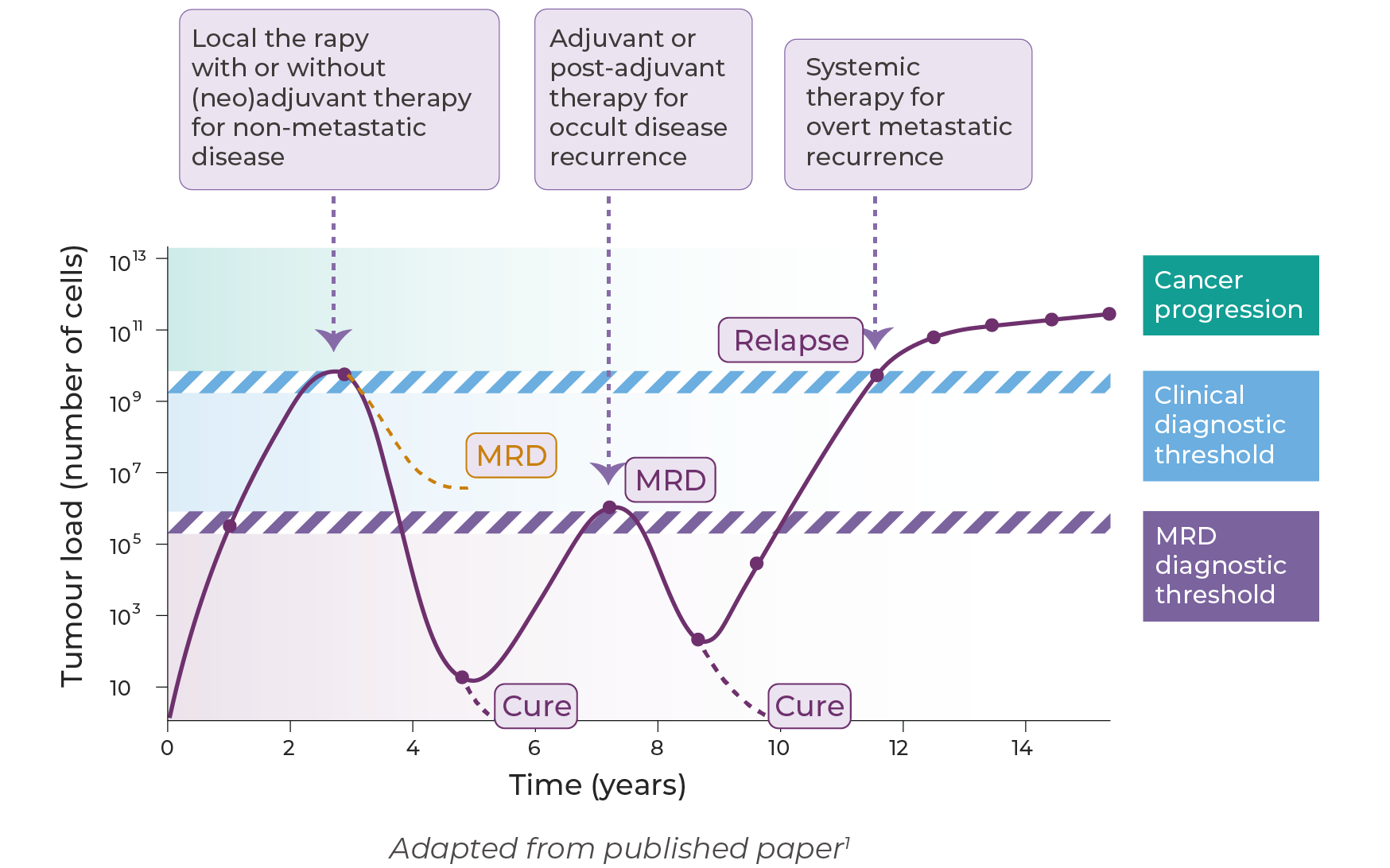
①Prognostic Stratification
Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Aug 2;28(15):3308-3317.
A positive MRD status after surgery or systemic therapy has been shown to strongly correlate with a higher risk of recurrence. High-sensitivity ctDNA-based MRD testing enables early identification of patients at increased risk, supporting more tailored post-treatment surveillance and improving prognostic accuracy at the molecular level. Its predictive power significantly surpasses that of conventional clinical risk factors, establishing MRD as a crucial molecular biomarker for prognosisnt[1].
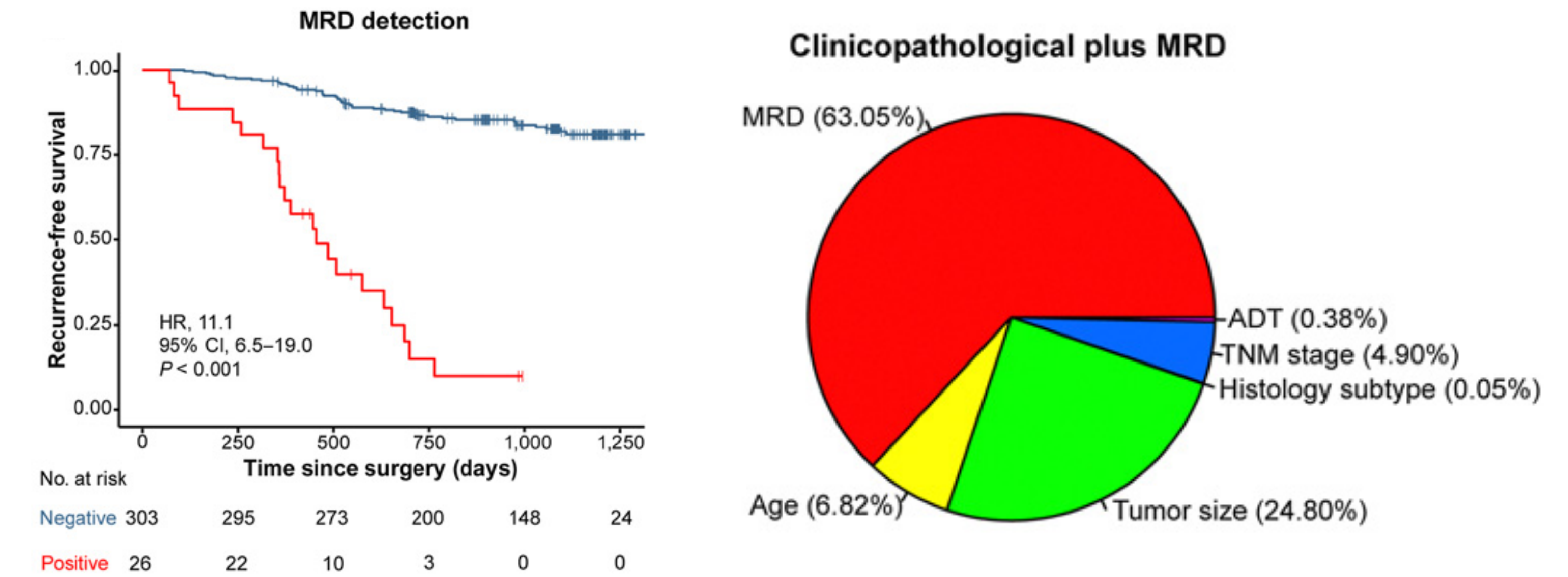
②Longitudinal Monitoring
J Natl Cancer Inst. 2025 Mar 25:djaf061.
MRD testing goes beyond single-point risk assessment—it enables longitudinal monitoring throughout the treatment journey. Serial ctDNA measurements provide real-time insight into molecular disease dynamics, improving the accuracy of recurrence prediction. Studies have shown that MRD positivity often precedes radiographic progression by several months, offering a critical window for earlier clinical intervention and more proactive patient management[2].
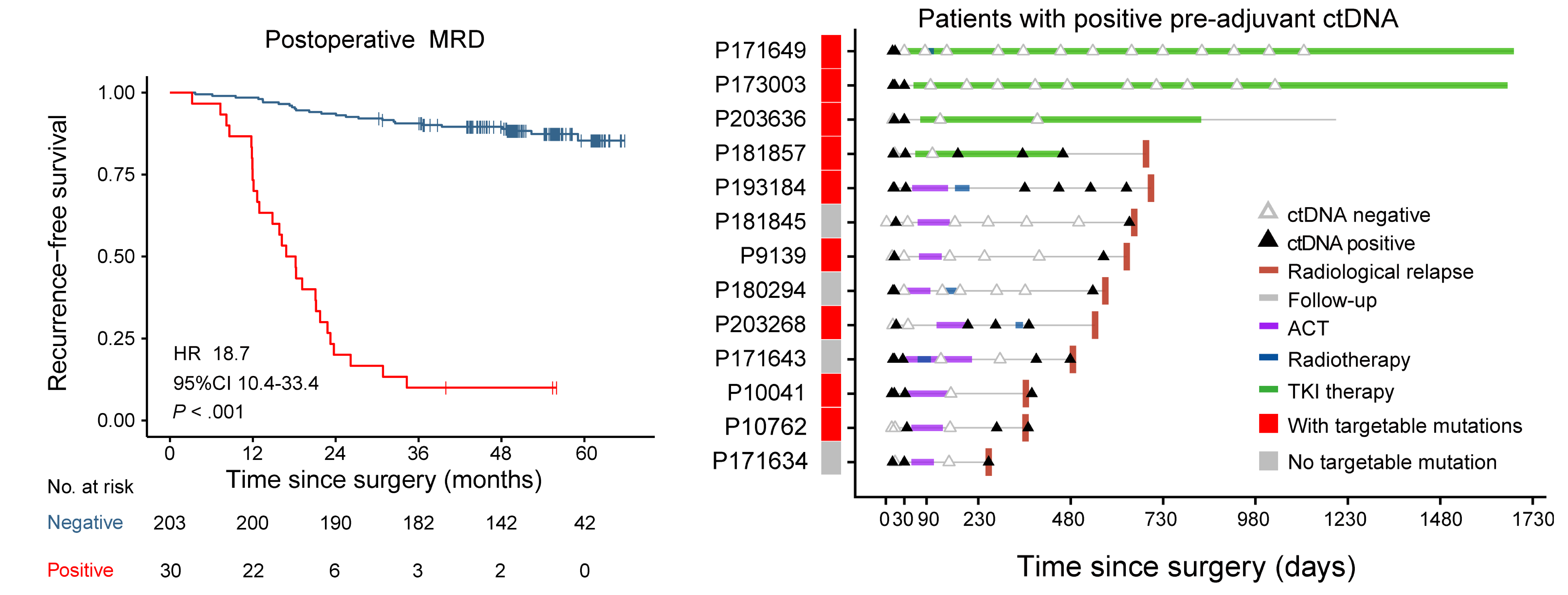
③Guiding Treatment Decisions
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020 Dec;17(12):757-770.
MRD is emerging as a critical molecular tool for guiding adjuvant therapy decisions after surgery. Multiple studies have demonstrated that MRD status can inform postoperative treatment strategies. In colorectal cancer, for example, the DYNAMIC studies showed that ctDNA-guided management significantly reduced the use of adjuvant chemotherapy in stage II patients without compromising recurrence-free survival. Furthermore, for MRD-positive patients, longitudinal ctDNA tracking enables adaptive treatment planning, helping clinicians tailor interventions to individual risk profiles and improving the precision of therapeutic decision-making[3].
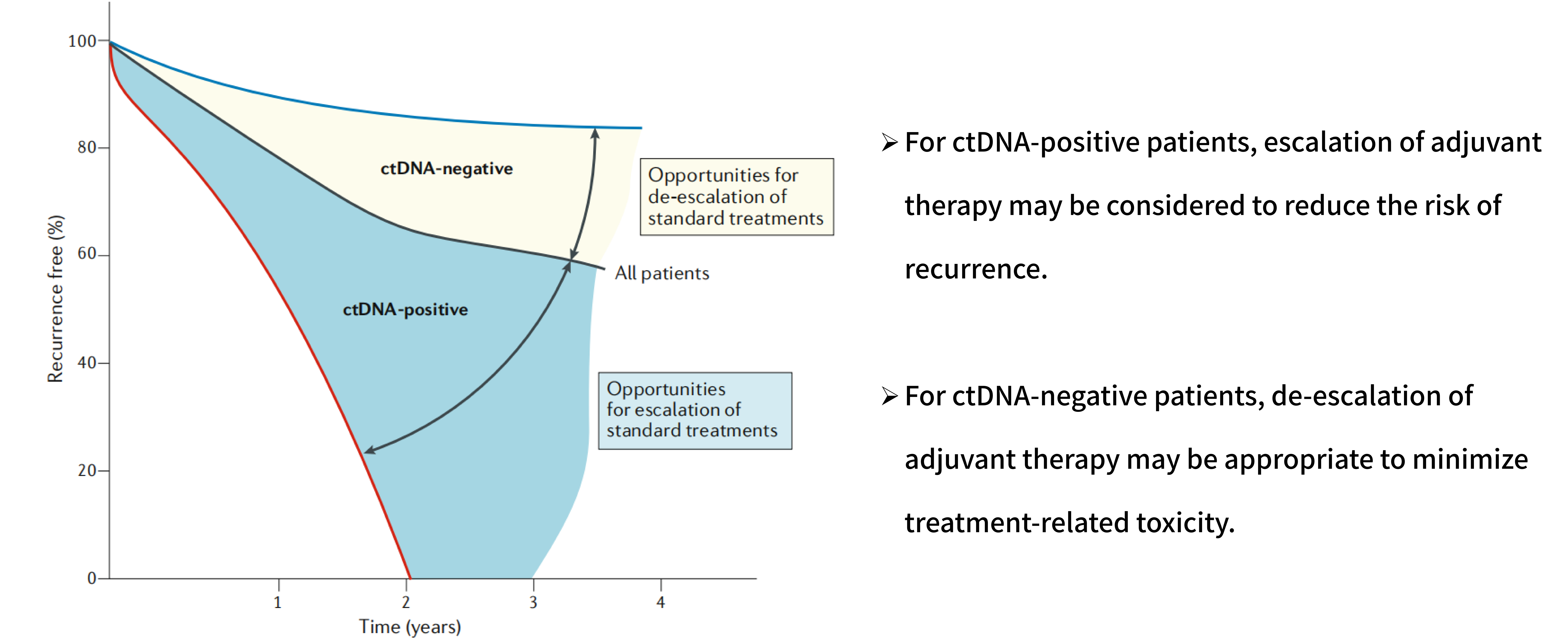
④Response Evaluation
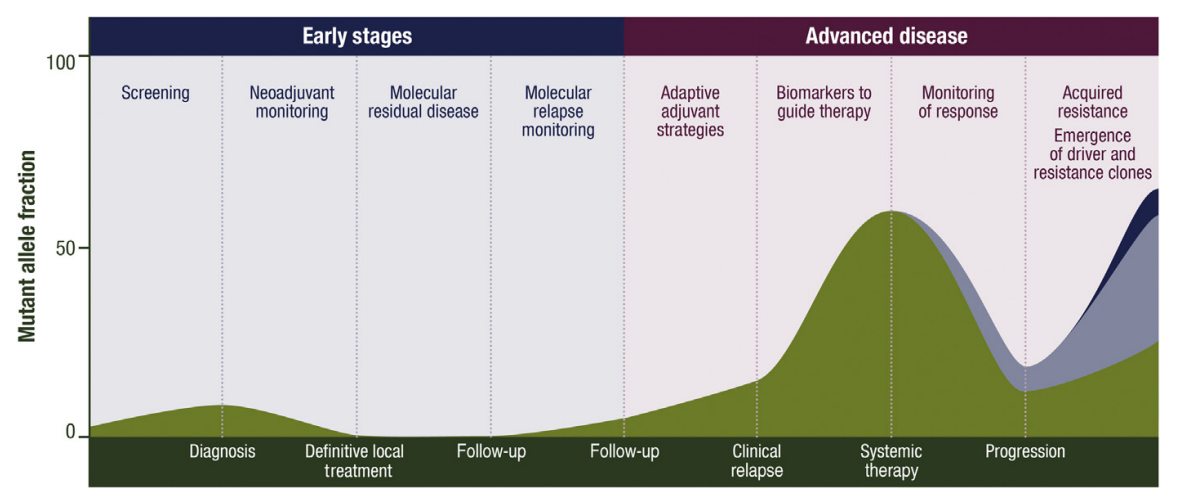
Ann Oncol. 2022 Aug;33(8):750-768.
sensitive molecular marker to dynamically assess treatment response. Conversion to MRD negativity often indicates effective therapy, while persistent or re-emergent MRD may signal emerging resistance, prompting timely intervention. In patients with stable disease on imaging, MRD can help identify those who are truly benefiting from treatment. Additionally, MRD status may support clinical decisions around treatment holidays, offering greater flexibility in long-term management[4].
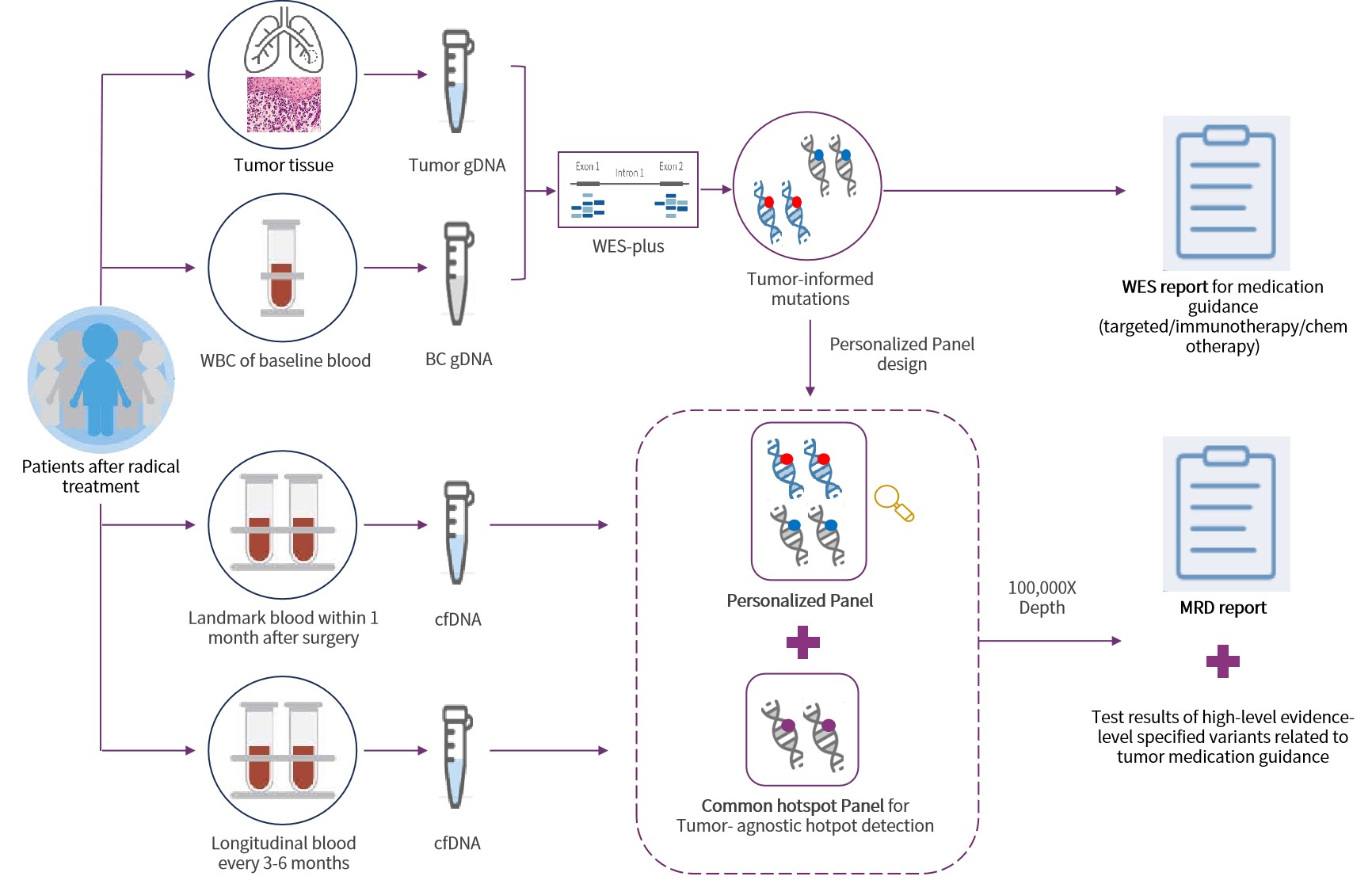
Technological Highlights Driving Clinical Confidence
Integrated Strategy. Dual Assurance. Precision in Every Decision.
WES Prime enhances key regions for both MRD and therapy guidance. Dual-panel design tracks MRD and captures emerging mutations.
Proprietary Algorithm. Clearer Signals.
Triple-layer noise suppression combined with the MinerVa Prime proprietary algorithm effectively filters background noise and sharpens ctDNA detection.
Beyond Standards. Designed for Excellence.
99.5% specificity and 0.0025% LoD—exceeding the 0.02% benchmark for earlier, more accurate detection.
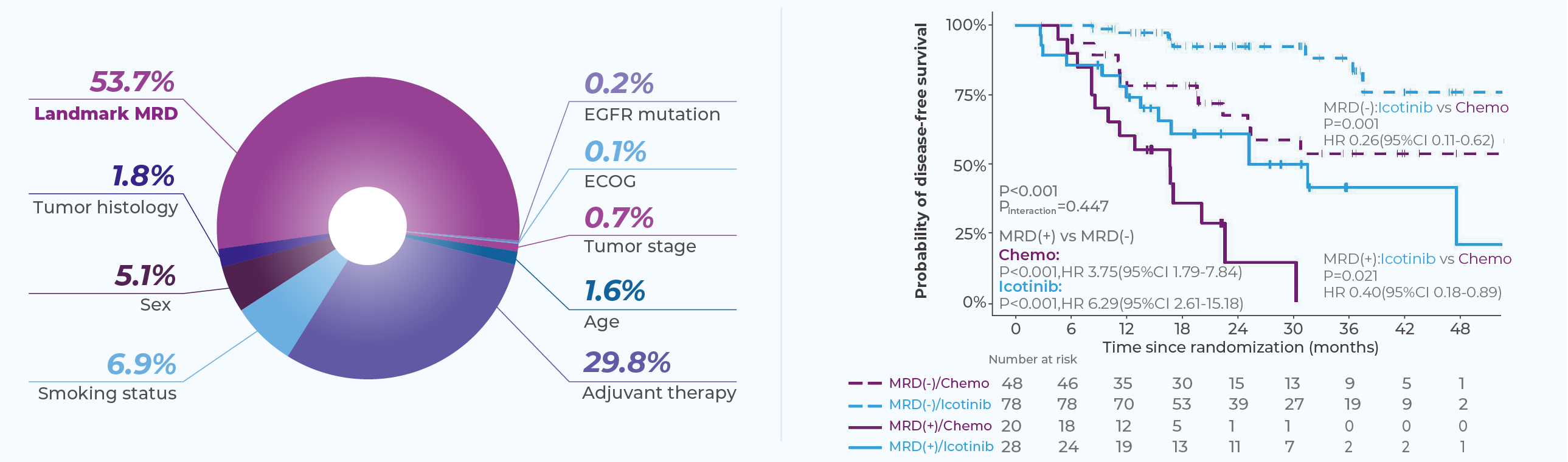
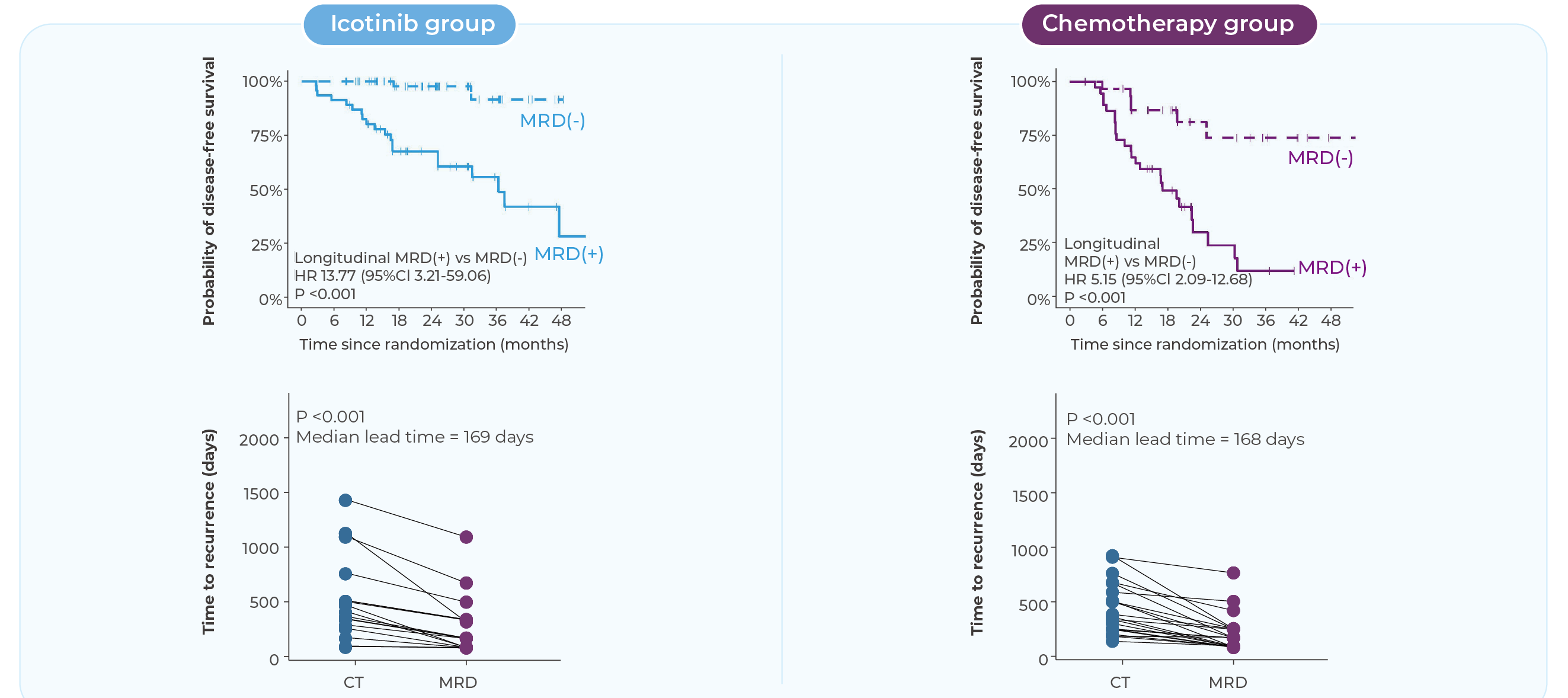
Clinically Validated in the EVIDENCE Trial[5]
MinerVa Prime was validated in the EVIDENCE study—the first large-scale randomized Phase III trial of adjuvant therapy in EGFR-mutant NSCLC among Chinese patients.
Interim data were presented at WCLC 2024. Dynamic MRD detection demonstrated a negative predictive value (NPV) of 91.3%, identifying recurrence a median of 168 days earlier than imaging.
Landmark MRD status has emerged as the most important prognostic biomarker during post-surgical follow-up.
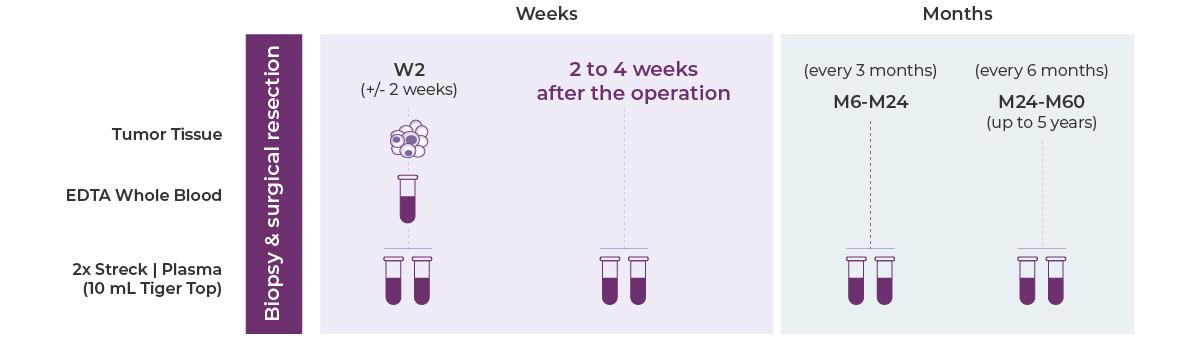
Testing Workflow & Ordering Process
TAT time:20 bussiness days*
((*) Turn-around time takes effect upon sample arrival at Genecast Singapore lab and clears sample quality checks.)
Step.1
To get started, send in your Genecast MinerVa Prime MRD requisition form, sign in to the online portal or talk to your sales representative.
Step.2
Please provide your tissue sample (FFPE block, more than 10 unstained slides, or wax roll), whole blood sample to the Genecast laboratory for baseline testing.
Step.3
Submit the patient's blood sample to the Genecast laboratory at physician-recommended time points for ctDNA-MRD testing.
Step.4
Qualified healthcare professionals will make treatment decisions based on the test results.
Q&A
What is MRD and why is it important?
MRD (Minimal Residual Disease) refers to the small number of cancer cells that may remain in the body after curative treatment, undetectable by conventional imaging. MRD is a key indicator of recurrence risk and can support early intervention and treatment planning.
Which cancer types are suitable for MRD testing?
MRD testing is widely applicable to various solid tumors, including lung, colorectal, breast, liver, prostate, and bladder cancers, among others.
When is the best time to perform MRD testing?
It is generally recommended to perform the first MRD test (Landmark timepoint) between 7–30 days after curative treatment to assess residual disease and stratify risk.
Recommended timepoints for longitudinal MRD monitoring:
Based on clinical research and expert consensus, MRD monitoring is recommended at the following stages:
1 month after surgery (Landmark MRD)
Mid-course of adjuvant therapy
At the end of adjuvant therapy
Every 3–6 months during follow-up, for up to 2–3 years
Longitudinal monitoring enables earlier detection of recurrence than imaging and supports timely clinical intervention.
What does a positive or negative MRD result mean?
MRD-positive: Indicates a higher risk of recurrence. Additional monitoring or treatment adjustments may be warranted.
MRD-negative: Suggests a lower risk of recurrence, but continued follow-up remains essential.
How does MRD testing differ from imaging?
Unlike imaging, MRD detects tumor-derived ctDNA in blood, often identifying molecular relapse months before radiographic evidence appears.
How sensitive and accurate is MRD testing?
Genecast MRD MinerVa Prime offers a limit of detection (LoD) as low as 0.0025%, with a specificity of over 99.5%, exceeding established clinical standards.
Is MRD testing suitable for all patients?
MRD testing is appropriate for most patients who have undergone curative-intent surgery or systemic therapy. Its use should be guided by the treating physician based on individual case assessments.
What are the limitations of MRD testing?
Results may be affected by factors such as sample quality and tumor heterogeneity. MRD findings should always be interpreted in the context of clinical judgment and other diagnostic tools.
Reference
[1] Perioperative ctDNA-Based Molecular Residual Disease Detection for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Prospective Multicenter Cohort Study (LUNGCA-1). Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Aug 2;28(15):3308-3317.
[2] Dynamic ctDNA informs whole-course postoperative precise management of NSCLC (LUNGCA study). J Natl Cancer Inst. 2025 Mar 25:djaf061.
[3] ctDNA applications and integration in colorectal cancer: an NCI Colon and Rectal-Anal Task Forces whitepaper. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020 Dec;17(12):757-770.
[4] RECIST ctDNA workshop group. Plasma ctDNA as a Treatment Response Biomarker in Metastatic Cancers: Evaluation by the RECIST Working Group. Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Nov 15;30(22):5034-5041.
[5] Fei Zhou | MRD predicts clinical outcomes of patients with early-stage EGFR-mutant NSCLC: a post-hoc biomarker analysis of EVIDENCE 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer.